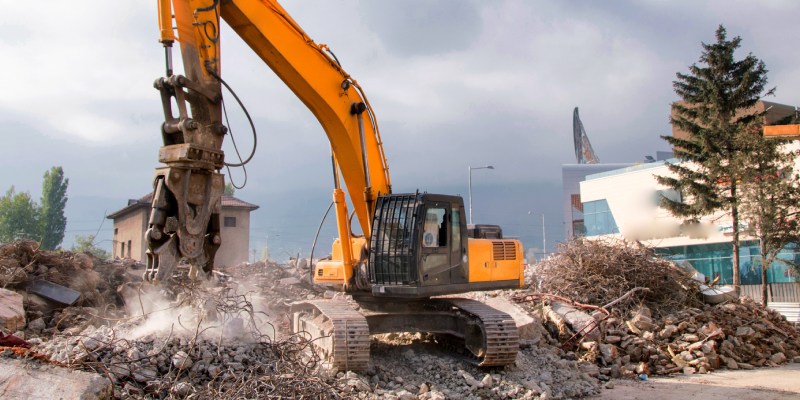
Demolition or dismantling refers to breaking up of buildings, structures either fully or partially . Utmost consideration is to be given to demolition or dismantling of structures than to erection, construction and maintenance. The problems, hazards and uncertainties can be much greater in demolition and it is also carried out by the unskilled workers.
The design engineers have responsibility for safety for not only for design and construction but also for the demolition of the structures at the end of its usual life.
Below we list our top 10 tips for staying safe on a demolition site.
Demolition Safety Tips

KEEP READING...
1. Be Asbestos Aware
Demolition and Refurbishment asbestos surveys and subsequent removal of licenced and non-licenced asbestos must be carried out before any demolition work can take place.
Only once all licenced and non-licenced asbestos has been removed can the demolition phase of a project begin.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Must Be Worn
As a minimum, 5-part PPE must be worn at all times on site by any operative. 5-Part PPE constitutes Hard Hat, Safety Glasses, High-Visibility Vest/Jacket, Safety Gloves, and Steel-Toe Cap Boots.
Required standards of PPE can vary, depending on the project being undertaken or a client’s specific requirements, and we ensure all our PPE satisfies each circumstance.
3. Prevent Accidents with Training, Qualification and Experience
Our training and qualification system for all employees is paramount to our Health, Safety and Environmental systems and procedures. All employees have the appropriate qualifications and experience for the assigned tasks they undertake and our site teams are closely monitored by Site Supervisors at all times.
This ensures all qualifications are in-date and that every operative is experienced in the duty they are carrying out, but also allows operatives to have a training plan so development can be encouraged as operatives become more experienced in the industry and therefore qualification standards can be improved as they progress.
4. Monitor Noise, Vibration and Dust
Environmental safety is also paramount on a demolition project. Noise, vibration and dust are common bi-products of demolition work and we ensure they are monitored and managed to minimise disruption to neighbouring parties to the site, and to minimise the effect on our own operatives.
5. A Clean Site is a Safe Site
Maintaining a clean and tidy site is a key factor in the successful and safe delivery of works on any demolition site. The surrounding area of a site is kept clean and tidy at all times. Measures such as road cleaning are actioned, if required. Housekeeping is paramount to promote a safe working environment and to also ensure that the demolition arisings and other materials from the site are dealt with appropriately. A safe site compound is imperative and welfare facilities are provided for operatives to take breaks away from the operational area of the site.
6. Manage Traffic Movement
Traffic Management Plans are established during the planning phase of a project and updated/amended as the works commence and progress on site. Segregation of pedestrians and vehicles is implemented, giving clear and unhindered pedestrian walkways and vehicle access to all required areas of site. Gatemen assist with flow and control of traffic on site and a stringent speed limit 5 mph is enforced. One-way systems are established to minimise the need for reversing and reversing cameras are on vehicles and plant to eliminate the need for operatives to be in close proximity to vehicles. Furthermore, traffic movements (including deliveries) are timed to avoid rush hour traffic at both ends of the day so no queuing of construction traffic will occur.
7. Manage Waste Disposal
Planning waste streams are identified as part of the risk assessment process and are a key safety measure on a demolition project. The control measures required are then selected to ensure that techniques, which assist the segregation and containment of the different materials, are used. Contingency plans are also made at this stage as to what precautions should be taken to minimise the potential for harm to be caused in the event of a spillage or other form of release.







Leave a Reply